Networks and telecommunications реферат
Обновлено: 05.07.2024
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminal nodes, links and any intermediate nodes which are connected so as to enable telecommunication between the terminals. The transmission links connect the nodes together. The nodes use circuit switching, message switching or packet switching to pass the signal through the correct links and nodes to reach the correct destination terminal.
Each terminal in the network usually has a unique address, so messages or connections can be routed to the correct recipients. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space.
the telephone network
the global Telex network
A telephone network is a telecommunications network used for telephone calls between two or more parties. There are a number of different types of telephone network:
· A landline network where the telephones must be directly wired into a single telephone exchange. This is known as the public switched telephone network or PSTN.
· A wireless network where the telephones are mobile and can move around anywhere within the coverage area.
· A private network where a closed group of telephones are connected primarily to each other and use a gateway to reach the outside world. This is usually used inside companies and call centers and is called a private branch exchange (PBX).
Public telephone operators (PTOs) own and build networks of the first two types and provide services to the public under license from the national government. Virtual Network Operators (VNOs) lease capacity wholesale from the PTOs and sell on telephony service to the public directly.
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators, providing infrastructure and services for public telecommunication. The PSTN consists of telephone lines, fiber optic cables, microwave transmission links, cellular networks, communications satellites, and undersea telephone cables, all interconnected by switching centers, thus allowing any telephone in the world to communicate with any other. Originally a network of fixed-line analog telephone systems, the PSTN is now almost entirely digital in its core network and includes mobile and other networks, as well as fixed telephones.
The technical operation of the PSTN adheres to the standards created by the ITU-T. These standards allow different networks in different countries to interconnect seamlessly. The E.163 and E.164 standards provide a single global address space for telephone numbers. The combination of the interconnected networks and the single numbering plan make it possible for any phone in the world to dial any other phone.
A wireless network is any type of computer network that uses wireless data connections for connecting network nodes. Wireless networking is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and enterprise (business) installations avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Wireless telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure. Examples of wireless networks include cell phone networks, Wi-Fi local networks and terrestrial microwave networks.
A cellular network or mobile network is a radio network distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, known as a cell site or base station. In a cellular network, each cell characteristically uses a different set of radio frequencies from all their immediate neighboring cells to avoid any interference.
When joined together these cells provide radio coverage over a wide geographic area. This enables a large number of portable transceivers (e.g., mobile phones, pagers, etc.) to communicate with each other and with fixed transceivers and telephones anywhere in the network, via base stations, even if some of the transceivers are moving through more than one cell during transmission.
Although originally intended for cell phones, with the development of smartphones, cellular telephone networks routinely carry data in addition to telephone conversations.
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM): The GSM network is divided into three major systems: the switching system, the base station system, and the operation and support system. The cell phone connects to the base system station which then connects to the operation and support station; it then connects to the switching station where the call is transferred to where it needs to go. GSM is the most common standard and is used for a majority of cell phones.
6. True, false or no information.
1.Telecommunications network nodes are connected via transmission links.
2. A public switched telephone network or PSTN is a radio network distributed over land areas.
3. A cellular network consists of telephone lines, fiber optic cables and undersea telephone cables.
4. The first global network was established using electrical telegraphy.
5. The GSM mobile communication network is used by over 6 billion people worldwide.
6. In a mobile network a large number of portable phones communicate with each other via base stations.
7. The PSTN includes now different networks.
7. Answer the questions.
1. What nodes does a telecommunication network consist of?
2. What switching do these nodes use?
3. What examples of telecommunications networks do you know?
4. How many types of telephone networks are mentioned in the text?
5. Who owns and builds landline network sand wireless networks?
6. How many systems is the GSM network divided in?
7. What standards allow different networks in different countries to interconnect?
8. What is a PBX?
9. What is the difference between PTOs and VNOs?
8. Continue the sentence.
1. A private network is…
a. a radio network distributed over land areas called cells.
b. usually used inside companies and call centers.
c. operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators.
2. Each terminal in the network has …
a. examples of telecommunications networks.
b. a different set of radio frequencies from all their immediate neighboring cells to avoid any interference.
c. a unique address, so messages or connections can be routed to the correct recipients.
3. GSM is the most common …
a. standard used for a majority of cell phones.
b. type of computer network that uses wireless data connections.
c. combination of the interconnected networks and the single numbering plan.
4. Wireless networking is a method …
a. to avoid any interference.
b. to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building.
c. to communicate with each other moving through more than one cell during transmission.
9. Match the words (1-6) with the definitions (A-G). Translate.
1. LAN. 2. PBX. 3. Wi-Fi 4. GPS. 5. PSTN. 6. GSM.
A.Public Switched Telephone Network. A country`s telephone network.
B.Private Branch Exchange. A telephone system bought and used by a company in their office.
C.A network which covers a small physical area, for example one building.
D.A system which uses radio signals to allow a broadband connection to the Internet.
E.A system which allows receiver to identify its position anywhere on earth.
G. A worldwide standard for mobile phones making phones from one operator compatible with a different operator in another country.
10. Make up a sentence using the words and phrases.
1. Decades, it, to set up, a global, takes, network. 2. In the network, called, is, the address space, the collection of addresses. 3. A huge, there, of different types, are, amount, of telephone networks. 4. For any phone in the world, it, possible, to dial any other phone, the combination of the interconnected networks, makes. 5. A lot of different tasks, perform, displaying e-books, can, many LCD e-readers, in addition to.
11. Find English equivalents.
Физические носители информации, требовать огромных усилий, установить глобальную сеть, достигнуть терминала, внутри зоны охвата, различный набор частот, использовать беспроводные информационные соединения, большинство сотовых телефонов, избегать помех, наземные телефонные сети, сложные телекоммуникационные узлы связи, общаться через базовые станции.
12. Translate into English. Use the construction „infinitive as attribute”.
Глобальная сеть, которую нужно установить; носители информации, которые будут использоваться; подводные кабели, которые следует изготовить; узел терминала, который будет заменен; помехи, которые необходимо устранить; уровень помех, который нужно достигнуть; беспроводные телефонные соединения, которые требуется обновить; качество сотовых телефонов, которое будет улучшаться; радио частоты, подлежащие изменению; зоны охвата, которые будут увеличены.
13. Translate into English.
1. Два дня тому назад мы посетили фирму, которая устанавливает наземные телекоммуникационные сети. 2. Cуществуют различные виды телекоммуникационных сетей.3. Нам показали оптоволоконные кабели, которые доходят до помещений клиентов. 4. Что качается меня, я предпочитаю использовать беспроводные сотовые телефоны. 5. Зона охвата этих устройств достаточно велика. 6. Кроме того, качество связи постоянно улучшается. 7. Cмоей точки зрения, самое лучшее качество предоставляет спутниковая связь.8. Использование этого вида связи позволяет нам
избежать помех. 9. В общем и целом следует внедрять все доступные телекоммуникационные технологии. 10. Мы должны также учитывать стоимость устройств, которые будут использоваться в области телекоммуникаций.
14. Give synonyms.
To span, collection, a set of laws, to establish, interference, storage, via, bugs, field of developing, to consist of, to exist, the costly process, to realize, to use, to join.
15. Translate into Russian. Explain the sequence of tenses.
1. They were informed yesterday that the company had paid all the accounts promptly. 2. The secretary said that she had prepared all the documents. 3. He informed the customers that their firm had ordered new equipment. 4. The sellers stated in their offer that orders were executed within six weeks. 5. The buyers stated in their enquiry that they had been cooperating with the firm since 2012. 6. The importers informed the suppliers that they wanted to know when delivery would be made, as the computers were urgently required.
16. Choose the correct voice. Translate.
1. Currently information technology (is impacting/is impacted) all walks of life all over the world. 2. Computerized databases are extensively (using/used) to store all sorts of confidential data of political, social, economic or personal nature to support human activities and bringing various benefits to the society. 3. However, the rapid development of information technology globally also (has led/has been leading) to the growth of new forms of national and transnational crimes. 4. These crimes (having/have) no boundaries and may (affect/affecting) any country across the globe. 5. The new boundaries, which (manifest/are manifested) in the monitor screen, passwords etc. have (created/been created) new personalities, groups, organizations, and other new forms of social, economic, and political groupings in the cyber world of bits.
17. Translate the following words into Russian. Say how they were formed.
Security-card-operated, day-to-day, word-processor, office-worker, risk-taking, ´export - ex´port, ´import – im´port, readable, installation, beautiful, helpless, disabled, misunderstand, understandable, briefly, impossible, aviator, amplify, amplifier, amplification.
- Для учеников 1-11 классов и дошкольников
- Бесплатные сертификаты учителям и участникам

Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:

NETWORKS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS Teacher: Ibraimova Assel

Purposes: to gaining knowledge of the fundamentals of construction, operation and use of computer networks of varying size, possibilities of their implementation on the basis of the underlying technologies and standards.

Glossary: EnglishRussianKazakh Networks and TelecommunicationsСети и телекоммуникации Желілер және телекоммуникациялар Network Сети Желі Computer networkКомпьютерные сети Компьютерлік желі Global computer network(GCS)Глобальная компьютерная сеть Ғаламдық компьютерлік желі Regional Networking (RCC)Региональная компьютерная сеть Аймақтық компьютерлік желі Local area network (LAN)Локальная сеть Жергілікті желі Separate class represent corporate computer networks (CCF)Отдельный класс представляют собой корпоративную компьютерную сеть Жекеленген корпоративтік желі Broadcast network configurationКонфигурация сети вещания хабар жүргізудің желілік конфигурациясы Topology network Топология сетиЖелі топологиясы

Brief description of terms: Computer network set of nodes (computers, terminals, peripherals) having the possibility of information exchange with each other using a special communication hardware and softwarenetwork with respect to peer access control to data paths in these networks distributed among the nodes. Network analyzer interception method as they move along the lines intranet connection Any part of the network resource or a network of computers (such as disk, directory, printer, etc.) that can used by the application during operation.

COMPUTER NETWORK A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network which allows computers to exchange data. In computer networks, networking devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media. The best-known computer network is the Internet.

Network computer devices that originate, route and terminate the data are called network nodes. Computer networks differ in the transmission medium used to carry their signals, communications protocols to organize network traffic, the network's size, topology and organizational intent. In the late 1950s early networks of computers included the military radar system Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE). In 1976 John Murphy of Datapoint Corporation created ARCNET, a token-passing network first used to share storage devices. In 1995 the transmission speed capacity for Ethernet increased from 10 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s. By 1998, Ethernet supported transmission speeds of a Gigabit. Subsequently, higher speeds of up to 100 Gbit/s were added (as of 2016).

Network topology Network topology is the layout or organizational hierarchy of interconnected nodes of a computer network.

IP address An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. The designers of the Internet Protocol defined an IP address as a 32-bit number and this system, known as Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is still in use today. IP addresses are usually written and displayed in human-readable notations, such as 172.16.254.1 (IPv4), and 2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:8:1 (IPv6).



The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP.

There are many different network structures that TCP/IP can be used across to efficiently route messages, for example: wide area networks (WAN) metropolitan area networks (MAN) local area networks (LAN) Internet area networks (IAN) campus area networks (CAN) virtual private networks (VPN)

LAN (local area network) is a group of computers and network devices connected together, usually within the same building. MAN (metropolitan area network) is a larger network that usually spans several buildings in the same city or town. WAN (wide area network), in comparison to a MAN, is not restricted to a geographical location, although it might be confined within the bounds of a state or country.

Wired technologies The orders of the following wired technologies are, roughly, from slowest to fastest transmission speed. Coaxial cable is widely used for cable television systems, office buildings, and other work-sites for local area networks. ITU-T G.hn technology uses existing home wiring (coaxial cable, phone lines and power lines) to create a high-speed (up to 1 Gigabit/s) local area network. Twisted pair wire is the most widely used medium for all telecommunication. An optical fiber is a glass fiber. It carries pulses of light that represent data.

Wireless technologies Terrestrial microwave – Terrestrial microwave communication uses Earth-based transmitters and receivers resembling satellite dishes. Communications satellites – Satellites communicate via microwave radio waves. Cellular and PCS systems use several radio communications technologies. Radio and spread spectrum technologies – Wireless local area networks use a high-frequency radio technology similar to digital cellular and a low-frequency radio technology. Free-space optical communication uses visible or invisible light for communications. In most cases, line-of-sight propagation is used, which limits the physical positioning of communicating devices.

Internet-based Self-services (ISS) are a subtype of services driven by self-service technologies which provide technological interfaces allowing customers to use services independently of the involvement of direct service employee. Self-ticket purchasing and self-check-in for a flight using the Internet are examples of Internet-based self-services.

QUESTIONS How long is an IPv6 address? What flavor of Network Address Translation can be used to have one IP address allow many users to connect to the global Internet? What are the two main types of access control lists (ACLs)? Which WLAN IEEE specification allows up to 54Mbps at 2.4GHz? Which of the following is the valid host range for the subnet on which the IP address 192.168.168.188 255.255.255.192 resides? What protocol does PPP use to identify the Network layer protocol? Which protocol does DHCP use at the Transport layer? Where is a hub specified in the OSI model?
Компьютеры появились в жизни человека не так уж давно, но почти любой
человек может с твердой уверенностью сказать, что будущее - за
компьютерными технологиями.
На заре своего появления компьютеры представляли собой громоздкие
устройства, работающие на лампах и занимающие настолько много места, что
для их размещения требовалась не одна комната.
Содержание
Введение
1.Компьютерные сети
2. Причины использования компьютерных сетей
3. Виды компьютерных сетей
4. Топологии компьютерных сетей
5. Обзор сетевых операционных систем
6. Телекоммуникации
7. Телекоммуникационная вычислительная сеть
8. Телекоммуникационные услуги
9. Internet
9.1 Преимущества
9.2 Недостатки
Заключение
Список использованной литературы
Прикрепленные файлы: 1 файл
Информатика.docx
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ
ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
студентка группы 1150
очной формы обучения
2. Причины использования компьютерных сетей
3. Виды компьютерных сетей
4. Топологии компьютерных сетей
5. Обзор сетевых операционных систем
7. Телекоммуникационная вычислительная сеть
8. Телекоммуникационные услуги
Список использованной литературы
Компьютеры появились в жизни человека не так уж давно, но почти любой
человек может с твердой уверенностью сказать, что будущее - за
На заре своего появления компьютеры представляли собой громоздкие
устройства, работающие на лампах и занимающие настолько много места, что
для их размещения требовалась не одна комната. При всем этом
производительность таких машин, по сравнению с современными, была
Время шло. Постепенно научная мысль и возможности ученых развились
настолько, что производство меньших по размеру, но более производительных
компьютеров стало реальностью.
Процесс развития персонального компьютера движется с постоянно
увеличивающимся ускорением, в связи с чем в ближайшем будущем компьютеры станут обязательным и незаменимым атрибутом любого предприятия, офиса и большинства квартир.
Причиной столь интенсивного развития информационных технологий является
все возрастающая потребность в быстрой и качественной обработки информации,
потоки которой с развитием общества растут как снежный ком.
Одной из наиболее перспективных на данный момент областей исследования
является разработка так называемых нейрокомпьютеров, основанных на
молекулах ДНК определенного вида водорослей, и способных хранить громадные объёмы информации относительно современного ПК при минимальных размерах
самих носителей информации.
Большой успех в последнее время получили так называемые виртуальные
технологии, которые позволяют с большой точностью моделировать физические
явления, процессы, предметы, а так же их взаимодействие в совокупности.
Такие технологии используются в различных областях деятельности человека.
Компьютерная сеть (вычислительная сеть, сеть передачи данных) — система связи компьютеров или вычислительного оборудования (серверы, маршрутизаторы и другое оборудование). Для передачи данных могут быть использованы различные физические явления, как правило — различные виды электрических сигналов, световых сигналов или электромагнитного излучения.
2. Причины использования компьютерных сетей
Компьютеры уже прочно вошли в современный мир, во все сферы человеческой деятельности и науки, тем самым создавая необходимость в обеспечении их различным программным обеспечением. Конечно, в первую очередь это связано с развитием электронной вычислительной техники и с её быстрым совершенствованием и внедрением в различные сферы человеческой деятельности.
Объединение компьютеров в сети позволило значительно повысить
производительность труда. Компьютеры используются как для производственных (или офисных) нужд, так и для обучения.
3. Виды компьютерных сетей
Существует три основных вида компьютерных сетей:
Локальные компьютерные сети (LAN – Local Area Network) – это сети, которые объединяют между собой компьютеры, находящиеся географически в одном месте. В локальную сеть объединяют компьютеры, расположенные физически близко друг от друга (в одном помещении или одном здании).
Региональные компьютерные сети (MAN – Metropolitan Area Network) – это сети, которые объединяют между собой несколько локальных компьютерных сетей, расположенных в пределах одной территории (города, области или региона, например, Дальнего Востока).
Глобальные вычислительные сети (WAN – Wide Area Network) – это сети, которые объединяют множество локальных, региональных сетей и компьютеров отдельных пользователей, расположенные на любом расстоянии друг от друга (Internet, FIDO).
Кроме того, каждая из перечисленных сетей может быть:
- Односерверной – сеть обслуживается одним файл-сервером (ФС);
- Многосерверной – сеть обслуживается несколькими ФС;
- Распределенной - Две или более локальных сетей, соединенных
внутренним или внешним мостами (мост или межсетевое соединение
управляет процессом обмена пакетами данных из одной кабельной
системы в другую). Пользователи распределенной сети могут
использовать резервы (такие как: файлы, принтеры или дисковые
драйвы) всех соединенных локальных сетей;
- Многосерверной локальной – когда локальная сеть обслуживается более
чем одним файл-сервером;
Также ЛВС могут быть одноранговыми (все компьютеры в сети
равноправны, т.е. нет ФС, Любая рабочая станция может получить доступ к
любой другой рабочей станции) и с централизованным управлением (выделенным
Локальная сеть - это группа компьютеров, которые могут
связываться друг с другом, совместно использовать периферийное
оборудование (например, жесткие диски, принтеры и т.д.) и обращаться к
удаленным центральным ЭВМ или другим локальным сетям. Локальная сеть
может состоять из одного или более
файл-серверов, рабочих станций и периферийных устройств. Пользователи сети
могут совместно использовать одни и те же файлы (как файлы данных, так и
станциями и защищать файлы с помощью мощной системы защиты.
Основными видами локальных вычислительных сетей являются Ethernet и
ARCNET. Причем Ethernet может иметь несколько типов кабеля:
- тонкий кабель Ethernet – иначе называется “Thinnet”. Имеет ряд
преимуществ, таких как использование более дешевого кабеля по
сравнению с системой толстого кабеля Ethernet и использование
аппаратуры, которую проще устанавливать;
- толстый кабель Ethernet (также известная как “Thicknet”) получила
свое название благодаря используемому в ней стандартному, или
толстому кабелю Ethernet. Толстый кабель позволяет включать в
систему большее количество компьютеров и увеличивать расстояние
между компьютерами. Однако этот кабель дороже, а его установка
сложнее по сравнению с тонким кабелем Ethernet;
- витая пара Ethernet. Преимущество системы Ethernet на витой паре в
том, что кабель дешевле по сравнению с перечисленными выше
кабелями, а его установка проще.
Наравне с приведенными выше способами подключения встречается способ
Token-ring. Одним из преимуществ системы является прогнозируемость: одна
часть системы может испортиться, но все-таки не остановится. Также, система
поддерживается программным обеспечением для больших ЭВМ фирмы IBM, что
может в некоторых ситуациях принести выгоду. Слабые стороны системы в
сравнении с другими системами заключаются в дороговизне и усложненности
кабелей. К тому же, в некоторых случаях трудно вести поиск неисправностей.
Региональная сеть – это города, объединенные в сеть посредством
расположенных в них компьютерах.
К глобальной вычислительной сети следует отнести Internet. На данный
момент это единственная сеть, объединяющая целые государства. На данный
момент американскими компаниями ведутся разработки по созданию
альтернативной глобальной сети.
4. Топологии компьютерных сетей
Физическое расположение компонентов сети (кабели, станции, шлюзы,
разветвители и т.д.).
Имеется три основных топологии: звезда, кольцо и
В сетях с топологией "звезда" рабочие станции подключаются непосредственно к файл-серверу, но не соединены друг с другом.
В сети с топологией "шина" все рабочие станции и файл-сервер подключаются к центральному кабелю, называемому шиной.
5. Обзор сетевых операционных систем
В мире существует очень большое количество сетевых операционных систем.
Среди наиболее удачных из них хотелось бы отметить Unix, Novell NetWare и
Windows NT Server. Все эти системы позволяют организовывать файл-серверы,
вести картотеку пользователей, ограничивать права клиентов файл-сервера,
выделять ресурсы рабочим станциям. Каждая из этих систем удовлетворяет
критериям надежности, отказоустойчивости и что самое главное –
Помимо систем, главной функцией которых является организация файл-
сервера, существуют системы, обеспечивающие работу пользователя в сети. К
числу таких операционных систем следует отнести (в хронологическом порядке)
Novell DOS, Windows for Workgroups, Windows95-98, Windows NT Workstation.
Причем последние операционные системы содержат не только утилиты,
позволяющие осуществлять доступ к локальным сетям, но и утилиты доступа к
7. Телекоммуникационная вычислительная сеть
Телекоммуникационная вычислительная сеть (ТВС) - это сеть обмена и распределённой обработки информации, образуемая множеством взаимосвязанные абонентские систем и средствами связи. Средство передачи и обработки информации ориентированы в ней на коллективное использование общесетевых ресурсов, аппаратных, информационных, программных.
Абонентская система – это совокупность ЭВМ программного обеспечения периферийного оборудования, средств связи с коммуникационной подсетью вычислительной сети выполняющих прикладные процессы.
Коммуникационная подсеть или телекоммуникационная система – представляет собой совокупность физической среды передачи информации аппаратурных и программных средств обеспечивающие взаимодействие абонентской системы.
Прикладной процесс – это различные процедуры ввода хранения, обработки и выдачи информации выполняемые в интересах пользователей и описываемые прикладными программами.
Умножаемые двоичные числа наиболее просто реализуются в прямом коде. Произведение получатся путём сложения частных произведений представляющих собой разряды множимого сдвинуться влево в соответствии с позициями разрядов множителя. Частные произведения формируются путём сложения знаковых разрядов сомножителей. Возможные переносы из знакового разряда игнорируются.
Операции деления, как и в десятичной арифметике являются обратной операцией умножения.
Классификация ТВС также наиболее характерны функциональные информационные структурные признаки.
1.По степени территориальной рассредоточенности элементов в сети (абонентских систем, узлов связи) различают глобальные (государственные), региональные и локальные вычислительные сети (ГВС, РВС, ЛВС).
2.По характеру реализуемых функций делятся на вычислительные (обработка информации), информационные (для получения справочных данных по вопросам пользователей), информационно-вычислительные (смешанные), в которых в определённом непостоянном соотношении выполняются вычислительные и информационные функции.



























Networking Computer network A collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources Usually, the connections between computers in a network are made using physical wires or cables However, some connections are wireless, using radio waves or infrared signals
Networking The generic term node or host refers to any device on a network Data transfer rate The speed with which data is moved from one place on a network to another Data transfer rate is a key issue in computer networks
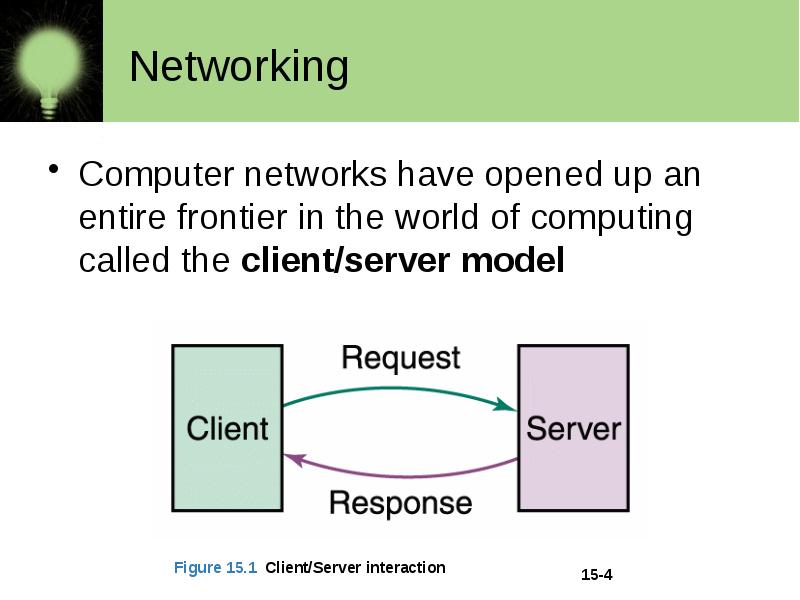
Networking Computer networks have opened up an entire frontier in the world of computing called the client/server model
Networking File server A computer that stores and manages files for multiple users on a network Web server A computer dedicated to responding to requests (from the browser client) for web pages
Types of Networks Local-area network (LAN) A network that connects a relatively small number of machines in a relatively close geographical area
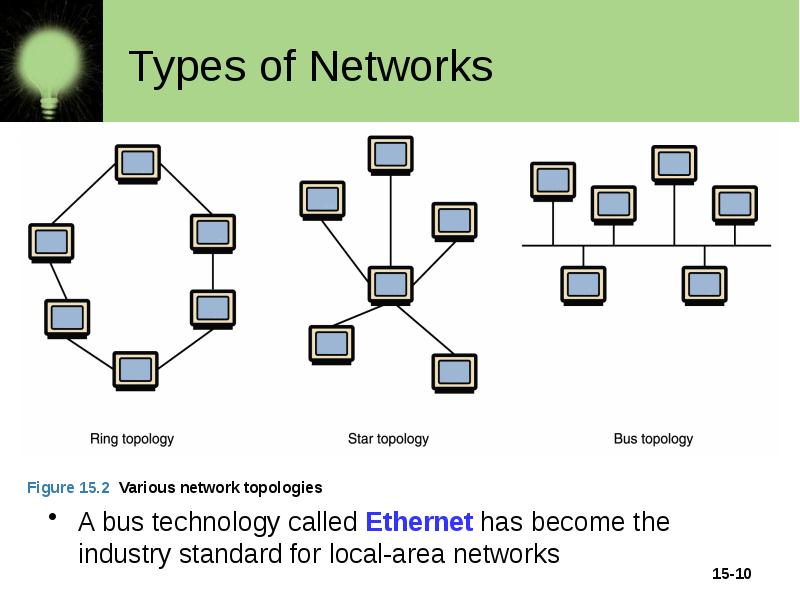
Types of Networks Various configurations, called topologies, have been used to administer LANs Ring topology A configuration that connects all nodes in a closed loop on which messages travel in one direction Star topology A configuration that centers around one node to which all others are connected and through which all messages are sent Bus topology All nodes are connected to a single communication line that carries messages in both directions
Types of Networks A bus technology called Ethernet has become the industry standard for local-area networks
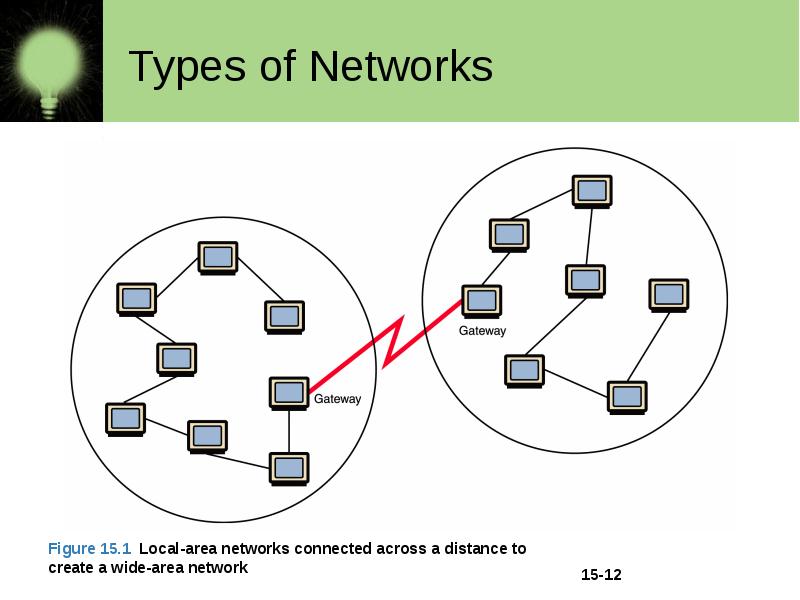
Types of Networks Wide-area network (WAN) A network that connects two or more local-area networks over a potentially large geographic distance Often one particular node on a LAN is set up to serve as a gateway to handle all communication going between that LAN and other networks Communication between networks is called internetworking The Internet, as we know it today, is essentially the ultimate wide-area network, spanning the entire globe
Types of Networks Metropolitan-area network (MAN) The communication infrastructures that have been developed in and around large cities
So, who owns the Internet? Well, nobody does. No single person or company owns the Internet or even controls it entirely. As a wide-area network, it is made up of many smaller networks. These smaller networks are often owned and managed by a person or organization. The Internet, then, is really defined by how connections can be made between these networks.
Internet Connections Internet backbone A set of high-speed networks that carry Internet traffic These networks are provided by companies such as AT&T, GTE, and IBM Internet service provider (ISP) A company that provides other companies or individuals with access to the Internet
Internet Connections There are various technologies available that you can use to connect a home computer to the Internet A phone modem converts computer data into an analog audio signal for transfer over a telephone line, and then a modem at the destination converts it back again into data A digital subscriber line (DSL) uses regular copper phone lines to transfer digital data to and from the phone company’s central office A cable modem uses the same line that your cable TV signals come in on to transfer the data back and forth
Internet Connections Broadband A connection in which transfer speeds are faster than 128 bits per second DSL connections and cable modems are broadband connections The speed for downloads (getting data from the Internet to your home computer) may not be the same as uploads (sending data from your home computer to the Internet)
Packet Switching To improve the efficiency of transferring information over a shared communication line, messages are divided into fixed-sized, numbered packets Network devices called routers are used to direct packets between networks
Open Systems Proprietary system A system that uses technologies kept private by a particular commercial vendor One system couldn’t communicate with another, leading to the need for Interoperability The ability of software and hardware on multiple machines and from multiple commercial vendors to communicate Leading to Open systems Systems based on a common model of network architecture and a suite of protocols used in its implementation
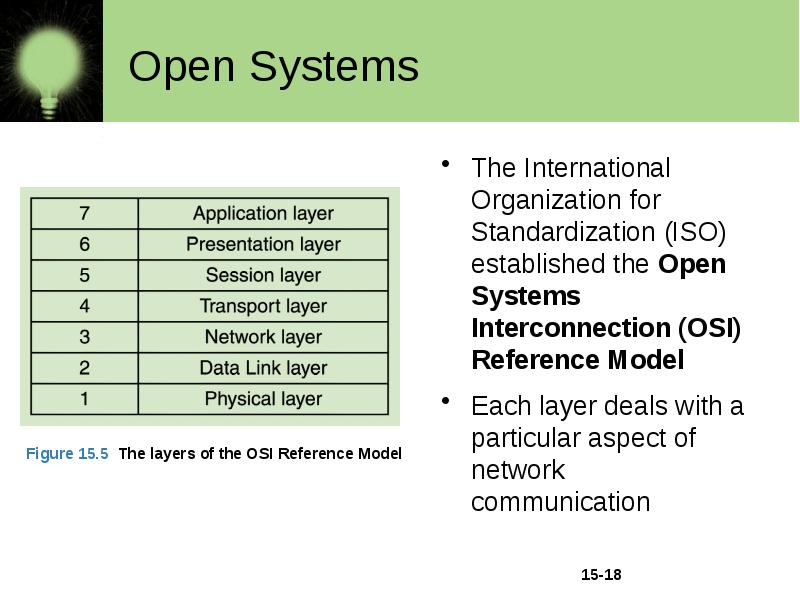
Open Systems The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model Each layer deals with a particular aspect of network communication
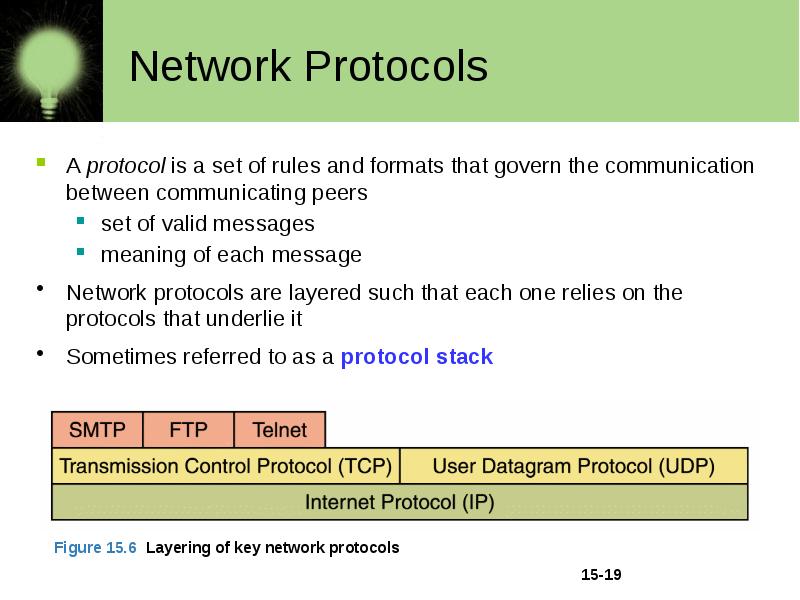
Network Protocols A protocol is a set of rules and formats that govern the communication between communicating peers set of valid messages meaning of each message Network protocols are layered such that each one relies on the protocols that underlie it Sometimes referred to as a protocol stack
TCP/IP TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol TCP software breaks messages into packets, hands them off to the IP software for delivery, and then orders and reassembles the packets at their destination IP stands for Internet Protocol IP software deals with the routing of packets through the maze of interconnected networks to their final destination
TCP/IP (cont.) UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol It is an alternative to TCP The main difference is that TCP is highly reliable, at the cost of decreased performance, while UDP is less reliable, but generally faster
MIME Types Related to the idea of network protocols and standardization is the concept of a file’s MIME type MIME stands for Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension Based on a document’s MIME type, an application program can decide how to deal with the data it is given
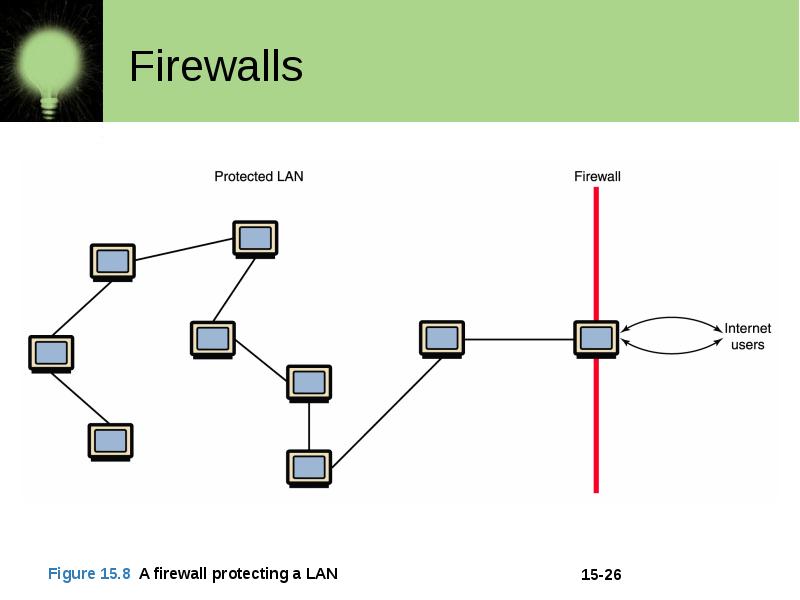
Firewalls Firewall A machine and its software that serve as a special gateway to a network, protecting it from inappropriate access Filters the network traffic that comes in, checking the validity of the messages as much as possible and perhaps denying some messages altogether Enforces an organization’s access control policy
Network Addresses Network software translates a hostname into its corresponding IP address For example 205.39.145.18
Network Addresses An IP address can be split into network address, which specifies a specific network host number, which specifies a particular machine in that network
Domain Name System A hostname consists of the computer name followed by the domain name csc.villanova.edu is the domain name A domain name is separated into two or more sections that specify the organization, and possibly a subset of an organization, of which the computer is a part Two organizations can have a computer named the same thing because the domain name makes it clear which one is being referred to
Domain Name System Organizations based in countries other than the United States use a top-level domain that corresponds to their two-letter country codes
Domain Name System The domain name system (DNS) is chiefly used to translate hostnames into numeric IP addresses DNS is an example of a distributed database If that server can resolve the hostname, it does so If not, that server asks another domain name server
Читайте также:

