The management of educational process planning educational process types of planning реферат
Обновлено: 05.07.2024
Testing becomes an important item and contextual base in educational process being a tool of problem solving. At the same time, it means effective introduction in all spheres of teaching and, accordingly, learning, productive methods of understanding the very core of education- prolonged development of a personality, open to new knowledge by definition.
There are many different opinions on the meaning and context testing in educational process, having much in common because testing is necessary, obligatory, useful, productive, effective and often very interesting method of correcting and clearing up not only the foreign language level, but level of personality, open to know the true stage of preparing in the subject and readiness to prolonged improvement in studying as a whole. “Prolonged” denotes “consistently”. Firstly it has attention to testing as a process and a separate problem of measuring od reliability of gotten volume of knowledge.
In educational process the teachers deal with their students abilities’ definition, estimation, measuring, developing and adoption as suitable to be in the near future successfully introduced in the professional field process.
Testing is not only intellectual, but emotional and psychological training for those tested. It is identifying tool, so, it needs identifying approach to all positions , including types of tests , different kind of testing, their close and prolonged purposes (aims and goals in a sum), the number of tests due to their concrete task for precisely measuring the abilities of those we are interested in.
It is essential to define in the process of teachers’ planning the testing the concrete cases where the tests “are likely to influence teaching”.
The educational program is oriented to stocking the knowledge items on the line from the simplest to the most difficult and complicated, being in demand. So, it is very important to think over terminological raw in accordance with all concrete themes and chapters of the educational program.
The scientists all over the world did their best in order to create “a test of testing system” [1, p. 6]. It includes a lot of items and moments of testing activity the teachers have been used not only in daily teaching routine practice, but in the course of pedagogical experiments under the headline “Testing”.
Before describing in details the different purposes of testing at the different stages of studying the different aspects of the discipline “foreign language” let us pay attention to the so called “in a special way organized ecologically from the position of psychology, calmness and understanding sphere of testing: place, time, group.” [2, p. 171]. One of our tasks as those testing those tested, is to define their stability of “Being Oneself” in any situation of control being close to risk-zone. In order to make the asking process comfortable and productive, some moments are to be taken into account while organizing the very calm space, where the role of all involved is equal for strong students and weak students. In this situation a teacher acts as the wise leader. His/her mission is to create a climate of success as possible and approved for everyone. At the same time, when testing is a kind of risk and stress, failure considers to be possible in order to break competition and jealousy. Everybody, strong or weak at the moment of testing is worth of being respected, because testing is one of the educational process’ actions, nor the educational personal result as a whole. So, there is always chances, possibilities and opportunities to improve the result, even not very good at the beginning. A special note deserves behavior. The wise leader-teacher pays respectful attention to all behavior. The teacher, having fluently looked the first answers, discovering mistakes and errors, let the students to understand that “knowing certain facts is not more powerful than simple wisdom” [3, p. 5]. From the position of educational process and educational sphere “wisdom” for a student is a wide range of his intellectual and personal possibilities, opportunities and skills, at every moment open to realization through successful studying in spite of the difficulties on the way to education.
The students learn that effective action arises out of readiness to overcome obstacles and optimizing the ways of communication with teachers and classmates in order to raise their students’ professional competence in a clear sense of productive being in learning action. The students learn that testing is an effective action, arising out of industrious intentions, systematic studies and recognition of responsibility of everyone in reaching educational goals, closely connected nowadays with possession a number of competencies as a foundation of a professional stability. So, the group testing work is grounded in obvious and natural righteousness with explained and adopted rules and regulations for an effective groups’ including into the process of control.
The source of the teachers ‘ability influences directly the students’ ability to be successful in testing. At every moment of his/her professional activity, a teacher is leading a group, being aware of what is happening and how estimating things happen. Due to this approach to the process a teacher can steer clear of trouble (satisfactory or bad marks of the students), and be both vital and effective. Even when a teacher does not write or answer a test on his/her own, he has to act accordingly. What does it mean? It means, that for the students’ testing as a process and means- denotes universality, telling all about their professionalism and personal value for their teacher, who is for them a source of power, endurance and excellence. That is why, consciousness or awareness, as the source of teacher’s ability, support the students, being testing, while learning them to become increasingly conscious and successful.
Let us come back to the purposes of testing, being recognized as obligatory at all stages of learning foreign language. The stages of the process may be described in a such consequence:
– to diagnose students’ weaknesses and strengths. It is necessary to identify what they do not know and what they know;
– to identify the stage of a teaching program, some parts of it due to the abilities of the students as most appropriate to;
– to assist placement of students of different level of preparation by preliminary individual personal testing them before a general testing of a whole group;
– to define the objectives of a course of study and declare it before forming the content of the testing materials’
– to discover how far students have achieved the objectives of a course of study;
– to define the frame of the language proficiency for the students of different level of preparation;
– to measure language proficiency regardless of any language courses that students, and then- specialists- may have followed;
– to create a system of estimation the results of testing with valuable advice to improve the results if necessary and detailed description of the way of achieving the high results in the course of the following testing.
This is a short structure of objective and subjective testing, showed good results in the course of pedagogical experiments with the students of different years of studying. The final stage included two kinds of tests - final achievement tests and progress achievement tests. The both types appeared to be very effective in the process of post-graduate teaching and professional training of specialists of the wide profile, being in great demand of a modern society. In reality. Testing is a noble labor, preparing winners. “Jucundi acti Labores sunt” (Труд завершенный приятен). “Industriae nil impossibile est” (Для прилежного нет невозможного).
- Для учеников 1-11 классов и дошкольников
- Бесплатные сертификаты учителям и участникам

- Поможем развить концентрацию и внимание с раннего возраста
- Повысим гибкость и раскованность в общении
Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:

EFFECTIVE LESSON PLANNING, DELIVERY TECHNIQUES AND CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT SUGGESTIONS START

Menu Article Test preface Suggested practices

Preface Good lesson planning is essential to the process of teaching and learning. A teacher who is prepared is well on his/her way to a successful instructional experience. The development of interesting lessons takes a great deal of time and effort. As a new teacher you must be committed to spending the necessary time in this endeavor. menu

Preface It is also important to realize that the best planned lesson is worthless if interesting delivery procedures, along with good classroom management techniques, are not in evidence. There is a large body of research available pertaining to lesson development and delivery and the significance of classroom management. They are skills that must be researched, structured to your individual style, implemented in a teacher/learning situation, and constantly evaluated and revamped when necessary. Consistency is of the utmost importance in the implementation of a classroom management plan. menu

Preface All teachers should understand that they are not an island unto themselves. The educational philosophy of the district and the uniqueness of their schools should be the guiding force behind what takes place in the classroom. The school’s code of discipline, which should be fair, responsible and meaningful, must be reflected in every teacher’s classroom management efforts. menu

SUGGESTED PRACTICES Establish a positive classroom environment Make the classroom a pleasant, friendly place Accept individual differences Learning activities should be cooperative and supportive Create a non-threatening learning environment Organize physical space; eliminate situations that my be dangerous or disruptive Establish classroom rules and procedures and consistently reinforce them menu

SUGGESTED PRACTICES Begin lessons by giving clear instructions State desired quality of work Have students paraphrase directions Ensure that everyone is paying attention Ensure that all distractions have been removed Describe expectations, activities and evaluation procedures Start with a highly motivating activity Build lesson upon prior student knowledge menu

Maintain student attention Use random selection in calling upon students Vary who you call on and how you call on them Ask questions before calling on a student; wait at least five seconds for a response Be animated; show enthusiasm and interest Reinforce student efforts with praise Vary instructional methods Provide work of appropriate difficulty Demonstrate and model the types of responses or tasks you want students to perform menu

Use appropriate pacing Be aware of your teaching tempo Watch for cues that children are becoming confused, bored or restless; sometimes lesson have to be shortened Evaluate what has taken place in your lesson Summarize the lesson and focus on positive gains made by students; use surprise reinforcers as a direct result of their good behavior Determine if the lesson was successful; were goals accomplished? menu

Provide suitable seatwork Seatwork should be diagnostic and prescriptive Develop procedures for seeking assistance; have a “help” signal Develop procedures for what to do when finished Move around to monitor seatwork Vary methods of practice menu

Make a smooth transition into next subject Have materials ready for next lesson Maintain attention of students until you have given clear instructions for the next activity Do not do tasks that can be done by students (i.e. passing out paper or collecting assignments); use monitors Move around and attend to individual needs Provide simple, step-by-step instructions Utilize a freeze and listen signal, when necessary menu

Develop positive teacher/student relationships Set a good example; be a positive role model Create an exciting learning environment for all students Reward good behavior; create special activities that children will enjoy doing Correct misbehaviors; have consequences of disruptive behavior; communicate them to children Handling disruptions Keep is short and simple (KISS) Use a warning system Defer disruptive behavior proactively (eye contact, close space between you and student, use head/hand gestures) Help students be successful Use planned ignoring (and teach other student to also ignore) menu

TEST A teacher must be committed to spending the necessary time With pupils at school Preparing for a lesson Checking tests menu

What is the utmost importance in the implementation of a classroom management plan? Consistency Individual style menu

A teacher in classroom should be strict to maintain the discipline True False Not mentioned menu

To establish a positive classroom environment, a teacher should Divide pupils into some groups Not give individual tasks Introduce common rules, so-called regulations for a group menu

It’s not so necessary to begin lessons , explaining the plan of the lesson to pupils True False menu

To maintain student attention, a teacher should Ask them in a line Give individual tasks Be active menu

It’s important to plan lessons , according to the level of students knowledge True False menu

To maintain student attention, a teacher should use …. selection in calling upon students Random In turn menu
To make students' interested in subjects, a teacher should: be strict use stable structures of a lesson show enthusiasm and interest menu

difficulty of work should: grow gradually and constantly be appropriate menu

Should teacher demonstrate and model the types of responses or tasks to students? yes sometimes no, they should think over models of responses themselves menu

what pacing should a teacher keep? fast, non-stop rhythm during the whole lesson a teacher should be aware of his teaching tempo show and measured tempo menu

at the end of a lesson teacher should: set marks without explanation concentrate attention on weak and negative points of the lesson summarize the lesson and focus on positive gains made by students menu

A teacher should: be carefully prepared for a lesson work on the spot and improvise for students to be more interested menu

how should a teacher rule a lesson? a teacher should give freedom to students to create positive atmosphere a teacher should let pupils guess about the rules of activity a teacher should provide simple, clear, step-by-step instructions for every activity menu

should a teacher pay attention to particular needs of pupils? never, teacher should always keep the same tempo and shouldn't distract to smo's problems yes, a teacher should move around and attend to individual needs sometimes, some points must be resolved and some shouldn't be paid attention, everything depends on a student. menu

should there be some special working signals in a class? yes no menu

what kind of behavior should a teacher show? a teacher should be mild and kind a teacher should be set a good example; be a positive role model a teacher should be strict menu

The article is devoted to the planning of the educational process of military training of soldiers, sailors, sergeants and petty officers of the reserve in the institutions of higher education. It is determined that the process of military training – a set of sequential actions learning and for learners to achieve the desired result, the goal, on the basis of certain principles. The conditions of learning of students in the education and training programs. The determining requirement for the planning of the educational process of military training should be the professionalism and competence of graduates, who served in the army at the University. Planning of educational process of military training of students on programmes of training soldiers, sailors, sergeants and foremen of stock in institutions of higher education are presented in the form of an algorithm consisting of several key components: an analytical, energetic, control and diagnosis, assessment, corrective.
Происходящие социально-экономические, политические и духовные изменения в Российском государстве и его Вооруженных силах требуют новых подходов к военному обучению студентов по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в организациях высшего образования.
Основная цель военной подготовки студентов вузов по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса – обеспечить потребности Вооруженных сил (ВС) в военно-обученных мобилизационных ресурсах и накопление в запасе военно-обученного резерва, а также предоставление возможности молодым людям, получающим высшее образование в вузах страны, право самостоятельно выбрать один из способов исполнения конституционного долга по защите Отечества [6].
Новая система военной подготовки студентов вузов, разработанная и внедренная в 72 вузах с 1 сентября 2014 г. в соответствии с Посланием Президента Российской Федерации, стала реальным позитивным шагом, который позволил:
- Вооруженным силам России расширить возможности в подготовке специалистов по наиболее сложным и востребованным военно-учетным специальностям, обеспечить поддержание в необходимых объемах военно-обученного мобилизационного людского ресурса;
- студентам вузов обеспечить непрерывность обучения, получить качественную военную подготовку с практическим освоением военно-учетной специальности, исполнить конституционную обязанность по защите Отечества одновременно с получением высшего образования, расширить возможности по трудоустройству после окончания обучения, в том числе на государственную гражданскую или муниципальную службу [4].
Процесс военной подготовки – совокупность последовательных действий обучающих и обучаемых для достижения требуемого результата, поставленной цели, на основе определенных принципов. Подготовка студентов гражданских вузов по тем или иным военно-учетным специальностям является не только областью военно-педагогической деятельности, что связано с ее целями, задачами, содержанием, с ее специфической военной организацией, с военными и преподавательскими кадрами, но и деятельностью в сфере профессионального образования [7].
Планирование образовательного процесса предназначено для осуществления обучения по программам военной подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса граждан Российской Федерации, обучающихся в вузе по очной форме обучения по основным профессиональным образовательным программам высшего образования (ОПОП ВО). Военная подготовка студентов осуществляется в процессе их обучения в добровольном порядке на основании договора, заключаемого между студентом и Министерством обороны Российской Федерации об обучении по программе военной подготовки.
Планирование образовательного процесса
Обучение по программам подготовки солдат и сержантов запаса включает два этапа: первый – теоретический, который предусматривает получение военных знаний, навыков и умений в ходе обучения, второй этап – практический, суть которого заключается в проведении сборов на базе воинских частей в течение одного месяца.
Организация образовательного процесса по программам военной подготовки включает: отбор граждан для подготовки по военно-учетным специальностям, комплектование учебных групп; разработку и реализацию программ подготовки; организацию и проведение выпускных экзаменов; учебно-материальное обеспечение подготовки. Обучение студентов будет проходить на уже существующих при вузах военных кафедрах. К ним будут предъявлять те же требования, что и к тем, кто обучается по программам подготовки офицеров запаса. Так, студент должен будет пройти медицинский осмотр, конкурсный отбор, а потом – заключить с Минобороны контракт на обучение. После окончания обучения студенты должны будут пройти учебные сборы и стажировки, после чего им будут присваиваться звания солдат (матросов) или сержантов (старшин).
Получить военную подготовку смогут студенты, начиная со второго курса. Продолжительность обучения по военно-учетным специальностям на должностях рядовых составит 1,5 года, сержантов – 2 года, с последующим зачислением в запас ВС РФ. По итогам обучения студенты сдадут квалификационные испытания, а учебные сборы завершатся экзаменами по военно-учетной специальности. Все, кто не пройдет испытания, будут призваны в ряды ВС после окончания учебы в общем порядке.
Предварительный отбор граждан для подготовки по военно-учетным специальностям осуществляется представителями военных кафедр образовательных учреждений после определения их годности к военной службе по состоянию здоровья и профессиональной пригодности к подготовке по военно-учетным специальностям. С учетом заключений о годности граждан к военной службе по состоянию здоровья и их профессиональной пригодности к подготовке по военно-учетным специальностям, вынесенных соответствующими комиссиями, проводятся отбор по физической подготовке, далее формируются списки граждан с указанием возможности их подготовки по военно-учетным специальностям на очередной учебный год и распределения по потокам обучения. При этом учитываются наклонности гражданина, его гражданская специальность и опыт практической работы.
Решение задач по планированию образовательного процесса подготовки сержантов и солдат предполагает применение системного подхода на основе координации и интеграции всех видов деятельности в образовательной сфере [2; 3]. В системе военно-профессионального образования образовательный процесс занимает центральное место как основополагающая категория, направленная на профессиональную подготовку сержантов и солдат из числа студентов вуза. Целесообразно разработать методику интеграции программ военной подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в образовательные программы высшего образования вузов таким образом, чтобы изучение обучающимися учебных дисциплин по программе военной подготовки проводилось на базе знаний, получаемых ими в ходе освоения специальных дисциплин по основной профессиональной образовательной программе [5].
Определяющим требованием следует считать профессионализм и компетентность выпускников, проходивших службу в армии в вузе [9]. Привлекательность компетентностного подхода заключается в том, что он имеет практическую, исследовательскую, профессионально ориентированную направленность [1]. В современных условиях важным требованием к студентам, проходившим военное обучение по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в организациях высшего образования, является формирование не простых исполнителей, запрограммированных на решение стереотипных задач, а личностей творческих, способных к постановке и решению военно-профессиональных задач конструктивными и нестандартными способами. При этом под профессионализмом сержантов и солдат из числа студентов понимается готовность выполнять военно-профессиональную деятельность по определенной военно-учетной специальности (группе специальностей) с высоким качеством, а также способность обучать и воспитывать подчиненных.
Конкретная реализация учебных планов и программ, планов методической, воспитательной и научной работы обучающихся осуществляется факультетами военного обучения (ФВО) и военными кафедрами.
Образовательная деятельность преподавателя факультета военного обучения в университете включает:
- в учебной работе (по реализации профессионально-образовательных программ по военно-учетной специальности) – проектирование условий и способов достижения целей и задач военного обучения; проведение всех видов учебных занятий; организацию индивидуальной подготовки обучаемых; оценку результатов и коррекцию учебной работы;
- в воспитательной работе (по формированию профессионально важных качеств личности сержанта и солдата) – решение воспитательных задач в процессе военного обучения; оценку результатов и коррекцию воспитательной работы сержантов и солдат;
- в развитии профессионального мышления и творческих способностей сержантов и солдат из числа студентов – обеспечение условий и возможностей для реализации творческого развития личности;
- в морально-психологической подготовке сержантов и солдат из числа студентов к профессиональной деятельности – моделирование фрагментов будущей профессиональной деятельности в образовательном процессе;
- в методической работе – реализацию комплекса методических задач, направленных на повышение качества учебного процесса, профессионального и педагогического уровня преподавателей;
- в научной работе – осуществление научной работы преподавателей в сфере военного обучения и военно-профессиональной подготовки сержантов и солдат из числа студентов.
Государственные требования к минимуму содержания и уровню подготовки сержантов и солдат по конкретной специальности являются частью федеральных государственных образовательных стандартов высшего образования, разрабатываются и утверждаются в порядке, установленном правительством Российской Федерации. Квалификационные требования к выпускникам разрабатываются с учетом военно-учетной специальности (специализации), по которой организуется подготовка сержантов и солдат.
Учебные планы и учебные программы составляются непосредственно вузом и ФВО на основе федеральных государственных образовательных стандартов высшего образования и квалификационных требований по соответствующей военно-учетной специальности.
Основной задачей в планировании образовательного процесса по программам военной подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса является разработка концепции и реализация технологии управления качеством подготовки сержантов и солдат из числа студентов, что обеспечивает достижение высокого уровня профессионализма и компетентности выпускников вуза и посредством этого способствует обеспечению безопасности личности, общества и государства.
Таким образом, планирование образовательного процесса военного обучения студентов по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в организациях высшего образования может быть представлено в виде алгоритма [8], состоящего из нескольких ключевых блоков: аналитического, содержательного, управления и диагностики, оценочного, корректирующего (рисунок).
Аналитический блок связан с конкурсным отбором студентов для военного обучения по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в соответствии с требованиями к обучению, направлению, объему и специфике знаний, необходимых для военно-учетной специальности.
Содержательный блок ориентирован на процесс военного обучения по разработанному рабочему учебному плану военной подготовки в дополнение к рабочему учебному плану основного обучения в вузе. Рабочий учебный план военной подготовки может включать: военно-специальные (военно-технические) дисциплины, тактические и тактико-специальные дисциплины, общевоинские дисциплины, стажировки и практики, в том числе учебные военные сборы.
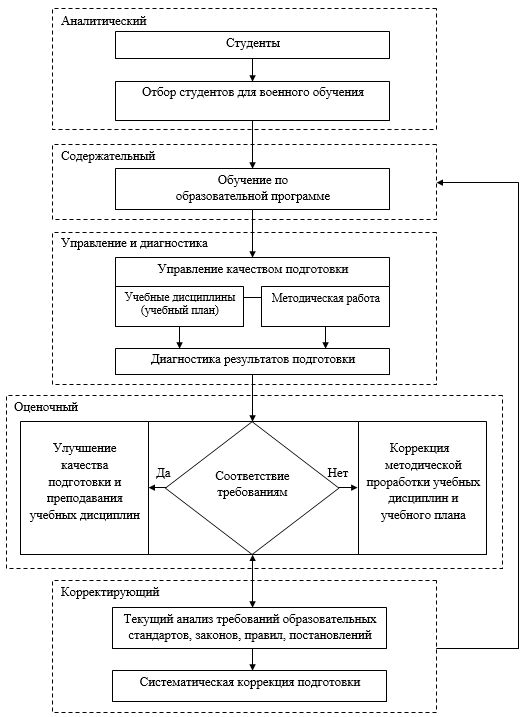
Алгоритм планирования образовательного процесса
Блок управления и диагностики отвечает за контроль процесса военной подготовки студентов (текущая успеваемость и посещаемость, рубежные контроли, контрольно-диагностические тренинги, промежуточная итоговая аттестация и др.), а также за методическую работу по подготовке методических указаний, учебных пособий и материалов для ведения учебного процесса.
Оценочный блок направлен на анализ результатов обучения, предполагая соответствие требованиям военного обучения студентов по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в организациях высшего образования по каждой военно-учетной специальности.
Корректирующий блок соотносит текущие требования законодательства, образовательных стандартов, правил, постановлений, требований к образовательному процессу с реальной практикой военного обучения студентов по программам подготовки солдат, матросов, сержантов и старшин запаса в организациях высшего образования, что позволяет проводить систематическую коррекцию образовательных программ и процесса обучения, а также своевременно принимать меры по исправлению недостатков в подготовке учащихся.
Профессионализм сержантов и солдат из числа студентов зависит в значительной степени от качества и результативности процесса его подготовки в вузе. Как отмечалось ранее, сложные и ответственные задачи стоят перед факультетом военного обучения в вузе на современном этапе реформирования системы военного образования. Эта система должна обеспечить подготовку сержантов и солдат из числа студентов с высокими профессиональными качествами, готовыми в любой момент встать на защиту суверенитета и государственных интересов России.

The process of development the higher education is closely connected with the improvement of the quality of training specialists process, with dynamically developing research and innovative education. The social environment and economic needs of university research is aimed at improving the education system and information technology. In the conditions of the modern world, the primary task of the education system is the training of highly qualified specialists that meet all the requirements of modern reality.
To improve the level of education in the credit system of education, it is necessary to form methods of increasing organizational and educational quality, as well as actively introduce pedagogical innovations. The education system should be supplemented by new content and tasks, modern conscious education and a new quality education that meets the high demands of the modern world.
Based on this approach, we can argue that in the process of preparing future specialists based on the credit system of education, innovation takes priority place. The relevance of this issue increases with the training of specialists whose activities are directly related to the creative process.
As a result of the introduction the credit training system changes to the training courses, the number of lecture hours were reduced, the main emphasis was placed on independent work carried out using a computer.
The credit system of training provides an opportunity for the learner to plan the educational process on his own. Educational work is assessed by the volume of the educational material, i.e. By credit.
The introduction of new educational technologies is connected with automation of educational and methodological complexes and plans and of course the selection of students by the trajectory, in the organizational automation of the educational process with the credit technology calculates the tutor's load- that is, in the use of information technology.
Today, information technologies are widely used in production, enterprises, document circulation and record keeping, the areas covered by these technologies are expanding day by day. According with this increase the volume and complexity of the information being processed, a new visualization has become necessary in the society.
The use of information technologies in the formation of professional competencies of future specialists is one of the basic requirements for modern information development of society. In the information society there is an objective need for specialists who are able to quickly adapt to the changing content of work activity, having the opportunity to quickly learn new knowledge and skills.
Qualitative improvement of the educational process is related to the educational information and the effective use of these technologies in the organization of the learning process. An important element in the formation of the student's professional competencies is information technology. Information technology means modern equipment and systems aimed at working with information and managing information processes.
Information technologies are widely used in science and practice, in various fields of education and production, including the educational process.
The use of information technology has a great influence on the formation of the scientific and potential of students, the development of their thinking skills, that is, in general, the training of specialists. On the basis of the use of information technologies in the educational process, students master such methods of scientific posing as formalization and modeling. Information technologies provide opportunities for the development of formal-logical and systemic forms of thinking, as well as the development of new methods of scientific knowledge. Therefore, today the issues of using information technologies are examined in detail in various spheres.
The analysis of scientific literature devoted to the study of the issues of information of education system shows that the cognitive operations of the management process, the content of the disciplines of higher education institutions, the environment, the forms and functions of instruction, the psychological and pedagogical characteristics acquire a new structure.
Due to the fact that 2/3 of the volume of the credit system curriculum includes the independent work of students, the need for using information technologies in organizing this process is increasing. The article deals with the possibilities of using information technologies in the organization of independent work by students of the credit form of education.
The analysis of scientific works and the practice of modern teaching proves that the value of independent work is characterized by the implementation by methodologists and teachers of methods and the ability of effectively demonstrate organizational forms. This connection is defined by a number of authors as a method of independent learning, a number of other authors as a means of teaching, and as a form of organizing the activity of students.
Some scientists analyzed the concept as following: «Independent educational activity is a didactic concept, an independent formulation of scientific and practical tasks, prediction and determination of one's own ways of solving them, based on self-control, self-assessment, and participatory actions of the participants in the pedagogical process. Knowledge of personality ".
According to the Kazakh scientist, the organization of independent work is related to the following conditions:
а) understanding a specific purpose of the work;
б) interest in the successful completion of work and its results;
в) performing work of one's own will, initiatives.
The main feature of the choice of technologies for organizing independent work is the need to build on the characteristics and predisposition of the student's personality, on his need for creative self-realization. The direction of strengthening the creative component of the personality of the future specialist requires from the disciplines of the university and the actions of the teacher to take into account the personality of the student, his values, interests and needs. In other words, the independent work of students should be based on the positions of learning directed at the person.
– Database management systems;
– editing menu with mathematical and statistical data;
– Using the menu for recognizing animations and texts.
- Using when performing independent work, algorithms and sample tasks, demonstrating examinations and presentations (computer, projector, video cameras, video clips).
- Special computer control programs, various testing programs are used to control independent work.
In the credit form of training, computer testing is widely used for the purposes of current, intermediate and final control. The consequence of improving the effectiveness of the educational process and the broad possibilities of modern information technologies is the automation of the pedagogical testing process.
The introduction of modern information technologies in the field of education leads to a qualitative change in the methods and types of organization of professional training for future specialists. For the effective organization of independent work by students, the use of electronic textbooks and methodological instructions becomes vital.
Within the educational process, the opportunities of information technologies and universal are widely used in the university, in particular, for the preparation of slide lectures and high-quality presentations, the capabilities of such universal applications as MS Power Point, Front Paige, Flash are used. The capabilities of the MS Power Point program provide students with access to the materials in the right amount. The manual, developed by the above methodology, is used not only during lecture classes, but also in the course of independent work. When doing independent work, students use information funds on the Internet. At the same time, students actively use the possibilities of electronic textbooks.
In general, the use of information technologies makes it possible to make significant changes in the information and methodological support of students' independent work. The main goal of the system of higher education is the preparation of highly qualified and competitive professionals through quality education based on modern education and pedagogical innovations. In such circumstances, the need for correct and effective use of information technology in the practice of future specialists is increasing. Therefore, the use of information technology has become the basis for the preparation of electronic educational publications for the organization of independent work of students.
Читайте также:

