Description of network topology of the office building реферат
Обновлено: 04.07.2024
Computers are connected to a single hub through a cable in the topology:
A) Mesh topology B) Bus topology C) Star topology
D) Tree topology E) Hybrid F) Ring topology
A) Moon topology B) Bus topology C) A circle topology
D) Mesh topology E) TREE topology F) Star topology
G) Hybrid topology
Network Topology exist:
A) Moon B) Bus C) A circle D) Line
E) Ring F) Bush G) Star
Computers are connected to a root node forming a hierarchy:
A) Moon B) Bus C) A circle D) Tree
E) Ring F) Bush G) Star
Command to view the IP- address of your computer:
An Internet service provider is:
A) an application program that provides a way to look at and interact with all the information
B) an organization that provides services for accessing in the Internet
C) Protocol for accessing Internet services
D) digital address of computer
E) Uniform Resource Locator
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is:
A) a reference to a web resource
B) Protocol for accessing Internet services
C) an application program for look at information
D) an organization for accessing in the Internet
E) communication between computers
URL consists of:
A) protocol B) IP-adress C) file name D) topology
E) domainname F) login G) password
Private cloud is used:
A) at the scale of single organization B) across multiple organizations
C) at the community of consumers from organizations that solve common problems
D) across the globe E) general public
Classification of computer networks by territory occupied:
A) corporate B) local C) custom D) parent
E) global F) specialized G) metropolitan
The e-mail address in the Internet: [email protected] "Name" of the computer on which the mail is stored:
A computer which is connected to the Internet must have:
A) IP Address B) Web server C) Home web page
D) Domain name E) Password F) Login
A computer connected to the Internet must have:
A) login B) domain name C) IP address
D) Password E) Web server
E-mail address consists of:
A) Username @ Domainname B) [email protected]
E) Iinternet [email protected] Domainname F) [email protected] Iinternet service
Слайды и текст этой презентации

LAN topologies
WAN topologies
Physical
Describes the geometric arrangement of components that make up the LAN
Logical
Describes the possible connections between pairs of networked end-points that can communicate

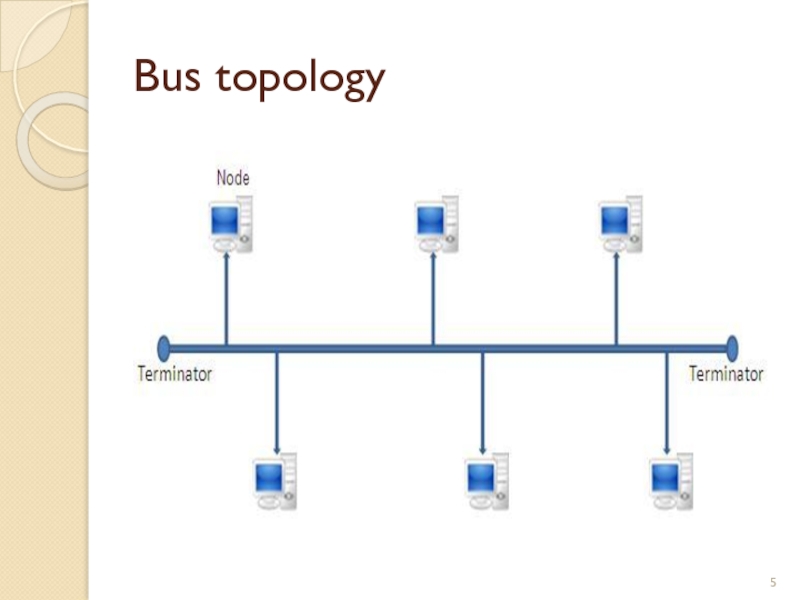
All networked nodes are interconnected, peer to peer, using a single, open-ended cable
Both ends of the bus must be terminated with a terminating resistor to prevent signal bounce

Advantages of Bus topology
Easy to implement and extend
Well suited for temporary networks that must be set up in a hurry
Typically the least cheapest topology to implement
Failure of one station does not affect others
Disadvantages of Bus topology
Difficult to administer/troubleshoot
Limited cable length and number of stations
A cable break can disable the entire network; no redundancy
Maintenance costs may be higher in the long run
Performance degrades as additional computers are added

started out as a simple peer-to-peer LAN topology
Each networked workstation had two connections: one to each of its nearest neighbors
Data was transmitted unidirectionally around the ring
Sending and receiving of data takes place by the help of TOKEN
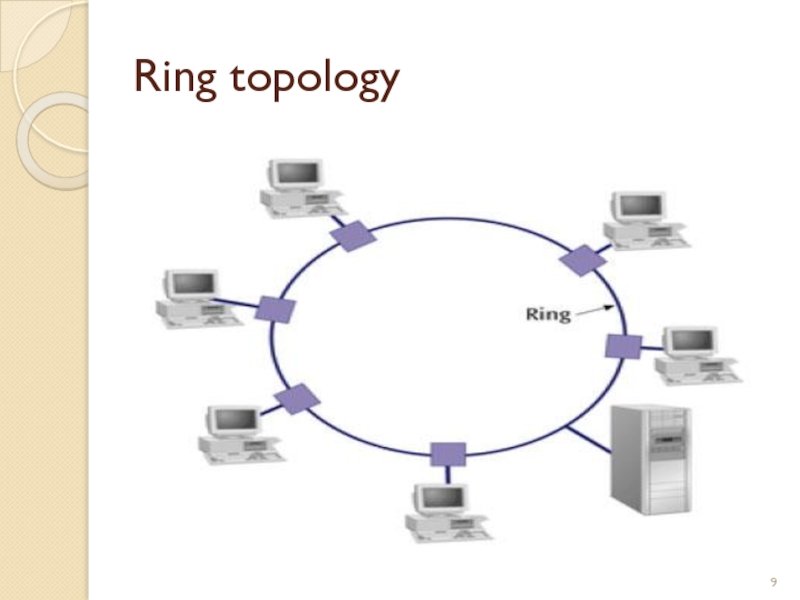

Advantages of Ring topology
This type of network topology is very organized
Performance is better than that of Bus topology
No need for network server to control the connectivity between workstations
Additional components do not affect the performance of network
Each computer has equal access to resources

Disadvantages of Ring topology
Each packet of data must pass through all the computers between source and destination, slower than star topology
If one workstation or port goes down, the entire network gets affected
Network is highly dependent on the wire which connects different components

Have connections to networked devices that “radiate” out form a common point
Each networked device in star topology can access the media independently
Have become the dominant topology type in contemporary LANs
Stars have made buses and rings obsolete in LAN topologies
- Для учеников 1-11 классов и дошкольников
- Бесплатные сертификаты учителям и участникам

Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:

NETWORKS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS Teacher: Ibraimova Assel

Purposes: to gaining knowledge of the fundamentals of construction, operation and use of computer networks of varying size, possibilities of their implementation on the basis of the underlying technologies and standards.

Glossary: EnglishRussianKazakh Networks and TelecommunicationsСети и телекоммуникации Желілер және телекоммуникациялар Network Сети Желі Computer networkКомпьютерные сети Компьютерлік желі Global computer network(GCS)Глобальная компьютерная сеть Ғаламдық компьютерлік желі Regional Networking (RCC)Региональная компьютерная сеть Аймақтық компьютерлік желі Local area network (LAN)Локальная сеть Жергілікті желі Separate class represent corporate computer networks (CCF)Отдельный класс представляют собой корпоративную компьютерную сеть Жекеленген корпоративтік желі Broadcast network configurationКонфигурация сети вещания хабар жүргізудің желілік конфигурациясы Topology network Топология сетиЖелі топологиясы

Brief description of terms: Computer network set of nodes (computers, terminals, peripherals) having the possibility of information exchange with each other using a special communication hardware and softwarenetwork with respect to peer access control to data paths in these networks distributed among the nodes. Network analyzer interception method as they move along the lines intranet connection Any part of the network resource or a network of computers (such as disk, directory, printer, etc.) that can used by the application during operation.

COMPUTER NETWORK A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network which allows computers to exchange data. In computer networks, networking devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media. The best-known computer network is the Internet.

Network computer devices that originate, route and terminate the data are called network nodes. Computer networks differ in the transmission medium used to carry their signals, communications protocols to organize network traffic, the network's size, topology and organizational intent. In the late 1950s early networks of computers included the military radar system Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE). In 1976 John Murphy of Datapoint Corporation created ARCNET, a token-passing network first used to share storage devices. In 1995 the transmission speed capacity for Ethernet increased from 10 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s. By 1998, Ethernet supported transmission speeds of a Gigabit. Subsequently, higher speeds of up to 100 Gbit/s were added (as of 2016).

Network topology Network topology is the layout or organizational hierarchy of interconnected nodes of a computer network.

IP address An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. The designers of the Internet Protocol defined an IP address as a 32-bit number and this system, known as Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is still in use today. IP addresses are usually written and displayed in human-readable notations, such as 172.16.254.1 (IPv4), and 2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:8:1 (IPv6).



The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP.

There are many different network structures that TCP/IP can be used across to efficiently route messages, for example: wide area networks (WAN) metropolitan area networks (MAN) local area networks (LAN) Internet area networks (IAN) campus area networks (CAN) virtual private networks (VPN)

LAN (local area network) is a group of computers and network devices connected together, usually within the same building. MAN (metropolitan area network) is a larger network that usually spans several buildings in the same city or town. WAN (wide area network), in comparison to a MAN, is not restricted to a geographical location, although it might be confined within the bounds of a state or country.

Wired technologies The orders of the following wired technologies are, roughly, from slowest to fastest transmission speed. Coaxial cable is widely used for cable television systems, office buildings, and other work-sites for local area networks. ITU-T G.hn technology uses existing home wiring (coaxial cable, phone lines and power lines) to create a high-speed (up to 1 Gigabit/s) local area network. Twisted pair wire is the most widely used medium for all telecommunication. An optical fiber is a glass fiber. It carries pulses of light that represent data.

Wireless technologies Terrestrial microwave – Terrestrial microwave communication uses Earth-based transmitters and receivers resembling satellite dishes. Communications satellites – Satellites communicate via microwave radio waves. Cellular and PCS systems use several radio communications technologies. Radio and spread spectrum technologies – Wireless local area networks use a high-frequency radio technology similar to digital cellular and a low-frequency radio technology. Free-space optical communication uses visible or invisible light for communications. In most cases, line-of-sight propagation is used, which limits the physical positioning of communicating devices.

Internet-based Self-services (ISS) are a subtype of services driven by self-service technologies which provide technological interfaces allowing customers to use services independently of the involvement of direct service employee. Self-ticket purchasing and self-check-in for a flight using the Internet are examples of Internet-based self-services.

QUESTIONS How long is an IPv6 address? What flavor of Network Address Translation can be used to have one IP address allow many users to connect to the global Internet? What are the two main types of access control lists (ACLs)? Which WLAN IEEE specification allows up to 54Mbps at 2.4GHz? Which of the following is the valid host range for the subnet on which the IP address 192.168.168.188 255.255.255.192 resides? What protocol does PPP use to identify the Network layer protocol? Which protocol does DHCP use at the Transport layer? Where is a hub specified in the OSI model?

Thanks for attention!
Краткое описание документа:
Computer network set of nodes (computers, terminals, peripherals) having the possibility of information exchange with each other using a special communication hardware and softwarenetwork with respect to peer access control to data paths in these networks distributed among the nodes.
A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network which allows computers to exchange data.
In computer networks, networking devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media. The best-known computer network is the Internet.
Топологии сетей | Курс "Компьютерные сети" (Февраль 2022).
Table of Contents:
В компьютерных сетях, топология относится к компоновке подключенных устройств. В этой статье представлены стандартные топологии сетей.
Топология в сетевом дизайне
Подумайте о топологии как виртуальной форме или структуре сети. Эта форма не обязательно соответствует фактическому физическому расположению устройств в сети. Например, компьютеры в домашней сети могут быть расположены по кругу в семейной комнате, но вряд ли найдет там кольцевую топологию.
Сетевые топологии подразделяются на следующие основные типы:
Более сложные сети могут быть построены как гибриды двух или более из вышеперечисленных базовых топологий.
Автобусная топология
Кольцевая топология
Для реализации кольцевой сети обычно используется технология FDDI, SONET или Token Ring. Кольцевые топологии встречаются в некоторых офисных зданиях или школьных кампусах.
Звездная топология
По сравнению с топологией шины сетевая сеть обычно требует большего количества кабелей, но отказ в любом сетевом сетевом кабеле приведет только к отключению сетевого доступа к компьютеру, а не всей локальной сети. (Однако, если хаб выходит из строя, вся сеть также терпит неудачу).
Топология деревьев
Топология дерева объединяет множество звездных топологий вместе на шину. В своей простейшей форме только узловые устройства подключаются непосредственно к древовидной шине, и каждый хаб функционирует как корень дерева устройств. Этот гибридный подход с шиной / звездой поддерживает будущее расширение сети намного лучше, чем шина (ограниченная количеством устройств из-за генерируемого широковещательного трафика) или звезда (ограниченная количеством точек подключения концентратора).
Топология сетки
Сетевая сеть, в которой каждое устройство соединяется со всеми, называется полной сеткой. Как показано на рисунке ниже, существуют частичные сетчатые сети, в которых некоторые устройства подключаются только косвенно к другим.
Резюме
Топология остается важной частью теории сетевого дизайна. Вероятно, вы можете построить домашнюю компьютерную сеть для дома или малого бизнеса, не понимая разницы между дизайном шины и дизайном звезды, но знакомство со стандартными топологиями дает вам лучшее понимание важных сетевых концепций, таких как концентраторы, трансляции и маршруты.
Как определить топологию в 3D-анимации

Топология в 3D относится к геометрическим характеристикам поверхности 3D-объекта. Подумайте об этом как о начале каркаса 3D-моделирования.
Введение в адаптеры компьютерной сети

Сетевой адаптер является важным компонентом любой компьютерной сети. Узнайте о различных типах аппаратного и программного обеспечения сетевого адаптера.
Введение в безопасность компьютерной сети

Со всеми жизненно важными персональными и бизнес-данными, которые каждый день делится с компьютерными сетями, безопасность стала важным аспектом сетевого взаимодействия.
Читайте также:

