How do americans regard their constitution доклад
Обновлено: 10.05.2024
После ознакомления с содержанием Топика ( Сочинения ) по теме " США " Советуем каждому из вас обратить внимание на дополнительные материалы. Большинство из наших топиков содержат дополнительные вопросы по тексту и наиболее интересные слова текста. Отвечая на не сложные вопросы по тексту вы сможете максимально осмыслить содержание Топика ( Сочинения ) и если вам необходимо написать собственное Сочинение по теме " США " у вас возникнет минимум сложностей.
Если у вас возникают вопросы по прочтению отдельных слов вы можете дважды нажать на непонятное слово и в нижнем левом углу в форме перевода есть отдельная кнопка которая позволит вам услышать непосредственно произношение слова . Или также вы можете пройти к разделу Правила Чтения Английского Языка и найти ответ на возникший вопрос.
The Constitution
The American Constitution is based on the doctrine of the separation of powers between the executive, legislative, and judiciary.
The respective government institutions — the Presidency, Congress, and the Courts — were given limited and specific powers; and a series of checks, whereby each branch of government has certain authority over the others to make sure these powers were not abused.
Government power was limited by means of a dual system of government, in which the federal government was only given the powers and responsibilities to deal with problems facing the nation as a whole (foreign affairs, trade, control of the army and navy, etc).
The remaining responsibilities and duties of government were reserved to the individual state governments.
Article V allowed for amendments to be made to the Constitution (once passed by a two-thirds majority in both houses of Congress and then ratified by the legislatures of three-fourths of the states).
The Constitution ratified by all thirteen states in 1791 already contained ten amendments, collectively known as the Bill of Rights (the freedoms of religion, speech, and the press, etc), to protect the citizens against possible tyranny by the federal government.
So far only twenty-six amendments have been made to the Constitution.
Конституция
Американская Конституция основана на доктрине разделения полномочий между исполнительной, законодательной и судебной ветвями.
Соответствующим правительственным институтом — президентству, Конгрессу, и судам — даны ограниченные и определенные полномочия; и ряд чеков и балансов, посредством чего у каждой ветви есть определенная власть над другими, также были включены, чтобы обеспечить то, чтобы этими полномочиями не злоупотребляли.
Правительственная власть была далее ограничена посредством двойной системы правления, при которой федеральному правительству дали только полномочия и обязанности иметь дело с проблемами, стоящими перед нацией в целом (иностранные дела, торговля, контроль над армией и флотом и т. д.).
Оставшиеся обязанности и полномочия правительства были оставлены правительствам отдельных штатов.
Статья V позволила делать поправки к Конституции (как только они пройдут большинством двух третей в обеих палатах конгресса и затем будут ратифицированы законодательными органами трех четвертей штатов).
Конституция, наконец ратифицированная всеми тринадцатью государствами в 1791 г., уже содержала десять поправок, вместе известных как Билль о правах (свобода религии, слова и прессы и т. д.), чтобы защитить гражданина от возможной тирании федерального правительства.
Пока только двадцать шесть поправок были внесены в Конституцию.
- Для учеников 1-11 классов и дошкольников
- Бесплатные сертификаты учителям и участникам

Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:


The Constitution of the United States of America is the supreme law of the United States. The Constitution is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.

The Constitution creates the three branches of the national government: a legislature, the bicameral Congress; an executive branch led by the President; a judicial branch headed by the Supreme Court. The Constitution specifies the powers and duties of each branch. The Constitution reserves all unenumerated powers to the respective states and the people, thereby establishing the federal system of government.

The Constitution is organized into three parts: Preamble - describes the purpose of the document and government Articles - establish how the government is structured and how the Constitution can be changed. There are seven articles. Amendments - changes to the Constitution; the first ten are called the Bill of Rights

The Constitution was adopted on September 17, 1787, by the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and ratified by conventions in each U.S. state in the name of "The People". The Constitution has been amended twenty-seven times; the first ten amendments are known as the Bill of Rights.

History of the Constitution During the Revolutionary War, the 13 colonies united. Delegates from each state got together and a plan for unity was initially submitted to the Second Continental Congress on July 12, 1776. After much debate, on November 15, 1777, the states finally established a "firm league of friendship" that became known as the Articles of Confederation. The Articles, however, did not go into effect until March 1, 1781. Under the Articles of Confederation, each state remained independent, with a single vote, and there was no real power behind the central government. The Articles of Confederation was weak – many people were in debt and states were printing money that was worthless. It was decided that the states should get together and fix the Articles and unite the states as one nation.


The Constitutional Convention A stronger central administration was needed if the nation was going to survive. Delegates from each state (except Rhode Island) began arriving in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in May 1787. The Philadelphia Convention

These articles helped sway public opinion. The Constitution was finally ratified and became legal on June 21, 1788. The Order of Ratification 1DelawareDecember 7, 1787 2PennsylvaniaDecember 12, 1787 3New JerseyDecember 18, 1787 4GeorgiaJanuary 2, 1788 5ConnecticutJanuary 9, 1788 6MassachusettsFebruary 6, 1788 7MarylandApril 28, 1788 8South CarolinaMay 23, 1788 9New HampshireJune 21, 1788 (With this state's signing, the Constitution became legal) 10VirginiaJune 25, 1788 11New YorkJuly 26, 1788 12North CarolinaNovember 21, 1788 (Initially voted against ratification) 13Rhode IslandMay 29, 1790 (Did not even hold a constitutional convention)

United States Bill of Rights

Influences on the Bill of Rights The United States Bill of Rights consists of the ten amendments added to the Constitution in 1791, as supporters of the Constitution had promised critics during the debates of 1788. The English Bill of Rights (1689) was an inspiration for the American Bill of Rights. Both require jury trials, contain a right to keep and bear arms, prohibit excessive bail and forbid "cruel and unusual punishments." Many liberties protected by state constitutions and the Virginia Declaration of Rights were incorporated into the Bill of Rights.

Preamble to the United States Constitution We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.


Article One: Legislative Power Article One describes the Congress, the legislative branch of the federal government. The United States Congress is a bicameral body consisting of two co-equal houses: the House of Representatives and the Senate.


Article Two: Executive power The section states that the executive power is vested in a President.

Article Three: Judicial power Article Three describes the court system (the judicial branch), including the Supreme Court. The article requires that there be one court called the Supreme Court; Congress, at its discretion, can create lower courts, whose judgments and orders are reviewable by the Supreme Court.
Article Four: States' powers and limits Article Four describes the relationship between the states and the federal government and amongst the states. For instance, it requires states to give "full faith and credit" to the public acts, records, and court proceedings of the other states. Congress is permitted to regulate the manner in which proof of such acts, records, or proceedings may be admitted.


Article Five: Amendments An amendment may be ratified in three ways: •The new amendment may be approved by two-thirds of both houses of Congress, then sent to the states for approval. •Two-thirds of the state legislatures may apply to Congress for a constitutional convention to consider amendments, which are then sent to the states for approval. •Congress may require ratification by special convention. The convention method has been used only once, to approve the 21st Amendment (repealing prohibition, 1933).

Article Six: Federal power Article Six establishes the Constitution, and the laws and treaties of the United States made according to it, to be the supreme law of the land, and that "the judges in every state shall be bound thereby, any thing in the laws or constitutions of any state notwithstanding.

Article Seven: Ratification Article Seven sets forth the requirements for ratification of the Constitution. The Constitution would not take effect until at least nine states had ratified the Constitution in state conventions specially convened for that purpose, and it would only apply to those states that ratified it

Judicial review The way the Constitution is understood is influenced by court decisions, especially those of the Supreme Court. These decisions are referred to as precedents. In the 1803 case Marbury v. Madison, the Supreme Court established the doctrine of judicial review. Judicial review is the power of the Court to examine federal legislation, executive agency rules and state laws, to decide their constitutionality, and to strike them down if found unconstitutional.

Amendments to the Constitution Since the original 10 amendments, the Bill of Rights as they are collectively known, 17 more amendments have been passed. The most recent, Amendment XXVII, was ratified May 2, 1992. Interestingly, it was originally proposed on September 25, 1789 and was one of the two that were not passed as part of the Bill of Rights. Amendment XXVII has to do with the compensation, or paying of a salary, to members of the Senate and House of Representatives. Other amendments have included: Amendment XIII, ratified on December 6, 1865, abolished slavery. Amendment XV, ratified on February 3, 1870, wherein "the right of the citizens…to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of race, color, or previous condition or servitude." Amendment XIX, ratified on August 8, 1920, which did much the same thing as Amendment XV, but was based on sex, basically giving women the right to vote. Only one amendment, Amendment XVIII, ratified on January 6, 1919, prohibiting "the manufacture, sale, or transportation of intoxicating liquors" was ever repealed. Amendment XXI, ratified on December 5, 1933, was the amendment that repealed Amendment XVIII.
Вы можете изучить и скачать доклад-презентацию на тему The Constitution of the USA.. Презентация на заданную тему содержит 18 слайдов. Для просмотра воспользуйтесь проигрывателем, если материал оказался полезным для Вас - поделитесь им с друзьями с помощью социальных кнопок и добавьте наш сайт презентаций в закладки!


















How united should the new states be? After the war for independence The most important disagreement was how to govern the new country. Some people wanted the nation to be a loose organization of states. They believed that citizens in each state should govern themselves. Others wanted a powerful national government to solve the problems of the new country. Each state had to give up some of its power so that the nation could be stronger.
Articles of Confederation (1781-1788). There was no president. National Congress (a lawmaking body) consisted of the Senate and the House of Representatives. Congress was given authority to declare war, to establish an army and navy, to issue and borrow money. The Articles gave most power to the states. Each one could cast one vote in Congress. A law could be passed only if nine of the thirteen states voted for it.
Articles of Confederation did not work well in practice. The states had too much power: They often acted like separate nations. Each state could coin its own money, arm its own soldiers and build its own navy. Each could, and sometimes did, make laws to hurt neighboring states. There was confusion about currency: Some used coins minted by the states, others used foreign coins, still others traded with goods like salt or pork. One of the biggest problems concerned foreign policy: Like any nation, the US needed to make treaties with foreign countries, but in 1785 most European nations did not respect American power.
Constitutional Convention In spring 1787 the states sent their 55 representatives to Philadelphia in order to take part in the Constitutional Convention and to write a new plan of government. This group included: George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, James Madison.
The project included Locke’s idea that the purpose of government is to protect natural rights of people to life, liberty and property. If a government fails to do so, the people have the right to rebel against it. Locke also rejected the belief that the power of kings came directly from God. He was convinced that political power came from the people. The idea that a government could only exist with the consent of the governed was also used by Madison. The latter included Rousseau’s statement that all citizens must take part in their government all the time. The principle from the Magna Carta that those who govern are subject to the law of the land as well as those who are governed, too. James Madison added the idea that private property should be the backbone of liberty.
The United States Constitution was adopted on September 17, 1787, by the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia.
The Constitution consists of: The preamble Seven original articles Twenty-seven amendments A paragraph certifying its enactment by the constitutional convention.
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. Preamble
On July 16, 1787 the plan of the new American government was completed. It created the House of Representatives and the Senate. Divided the political power among the three branches of government: The legislative branch The executive branch The judicial branch
Not all Americans approved of the constitution. It took almost a year before nine out of thirteen states ratified it as there was a strong opposition to the project. People feared that under the constitution the president would become as powerful as a king. They thought that states were the best defenders of the people’s liberties because state constitutions guaranteed personal freedoms, while the US constitution did not have a bill of rights.
“A bill of rights, is what the people are entitled to … and what no just government should refuse”. Wrote Thomas Jefferson in 1787, when found out that the constitution had no bill of rights
“A bill of rights” Madison helped to write 12 amendments, concerning the rights of the people. In December 1791, 10 of them became part of the constitution.
Under the new constitution the American nation would grow strong and united. George Washington was easily elected as the first US president. Cabinet of advisers consisted of 4 members: Thomas Jefferson Alexander Hamilton Henry Knox Edmund Randolph
Washington retired in 1796, after two terms of service. This decision set an example for future presidents. In his farewell address Washington asked that people forgive his mistakes and remember the good he had tried to do. Washington wanted Americans to support the union. He was against the growth of political parties which would divide the nation, against permanent alliances with foreign powers which could keep the nation from acting in its own best interests. Many Americans still consider that their first president was the best one.

№ слайда 1
The Constitution of the USA.

№ слайда 2
After the war for independence The most important disagreement was how to govern the new country.Some people wanted the nation to be a loose organization of states. They believed that citizens in each state should govern themselves.Others wanted a powerful national government to solve the problems of the new country. Each state had to give up some of its power so that the nation could be stronger.

№ слайда 3
Articles of Confederation (1781-1788). There was no president.National Congress (a lawmaking body) consisted of the Senate and the House of Representatives.Congress was given authority to declare war, to establish an army and navy, to issue and borrow money.The Articles gave most power to the states. Each one could cast one vote in Congress. A law could be passed only if nine of the thirteen states voted for it.

№ слайда 4
Articles of Confederation did not work well in practice. The states had too much power: They often acted like separate nations. Each state could coin its own money, arm its own soldiers and build its own navy. Each could, and sometimes did, make laws to hurt neighboring states.There was confusion about currency: Some used coins minted by the states, others used foreign coins, still others traded with goods like salt or pork.One of the biggest problems concerned foreign policy: Like any nation, the US needed to make treaties with foreign countries, but in 1785 most European nations did not respect American power.

№ слайда 5
Constitutional Convention In spring 1787 the states sent their 55 representatives to Philadelphia in order to take part in the Constitutional Convention and to write a new plan of government.This group included: George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, James Madison.

№ слайда 6
The project of the constitution was composed by James Madison.

№ слайда 7
The project included Locke’s idea that the purpose of government is to protect natural rights of people to life, liberty and property. If a government fails to do so, the people have the right to rebel against it. Locke also rejected the belief that the power of kings came directly from God. He was convinced that political power came from the people. The idea that a government could only exist with the consent of the governed was also used by Madison. The latter included Rousseau’s statement that all citizens must take part in their government all the time.The principle from the Magna Carta that those who govern are subject to the law of the land as well as those who are governed, too. James Madison added the idea that private property should be the backbone of liberty.

№ слайда 8
The United States Constitution was adopted on September 17, 1787, by the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia.

№ слайда 9
The Constitution consists of: The preamble Seven original articles Twenty-seven amendments A paragraph certifying its enactment by the constitutional convention.

№ слайда 10
Preamble We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.

№ слайда 11
On July 16, 1787 the plan of the new American government was completed. It created the House of Representatives and the Senate.Divided the political power among the three branches of government:The legislative branchThe executive branchThe judicial branch

№ слайда 12
Not all Americans approved of the constitution. It took almost a year before nine out of thirteen states ratified it as there was a strong opposition to the project.People feared that under the constitution the president would become as powerful as a king. They thought that states were the best defenders of the people’s liberties because state constitutions guaranteed personal freedoms, while the US constitution did not have a bill of rights.
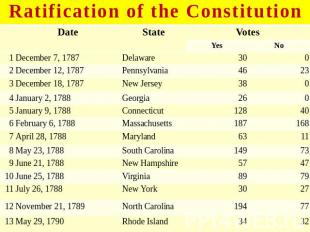
№ слайда 13

№ слайда 14
“A bill of rights, is what the people are entitled to … and what no just government should refuse”. Wrote Thomas Jefferson in 1787, when found out that the constitution had no bill of rights

№ слайда 15
“A bill of rights”Madison helped to write 12 amendments, concerning the rights of the people. In December 1791, 10 of them became part of the constitution.

№ слайда 16
Under the new constitution the American nation would grow strong and united. George Washington was easily elected as the first US president.Cabinet of advisers consisted of 4 members:Thomas Jefferson Alexander Hamilton Henry Knox Edmund Randolph

№ слайда 17

№ слайда 18
Washington retired in 1796, after two terms of service. This decision set an example for future presidents. In his farewell address Washington asked that people forgive his mistakes and remember the good he had tried to do. Washington wanted Americans to support the union. He was against the growth of political parties which would divide the nation, against permanent alliances with foreign powers which could keep the nation from acting in its own best interests. Many Americans still consider that their first president was the best one.
Читайте также:

